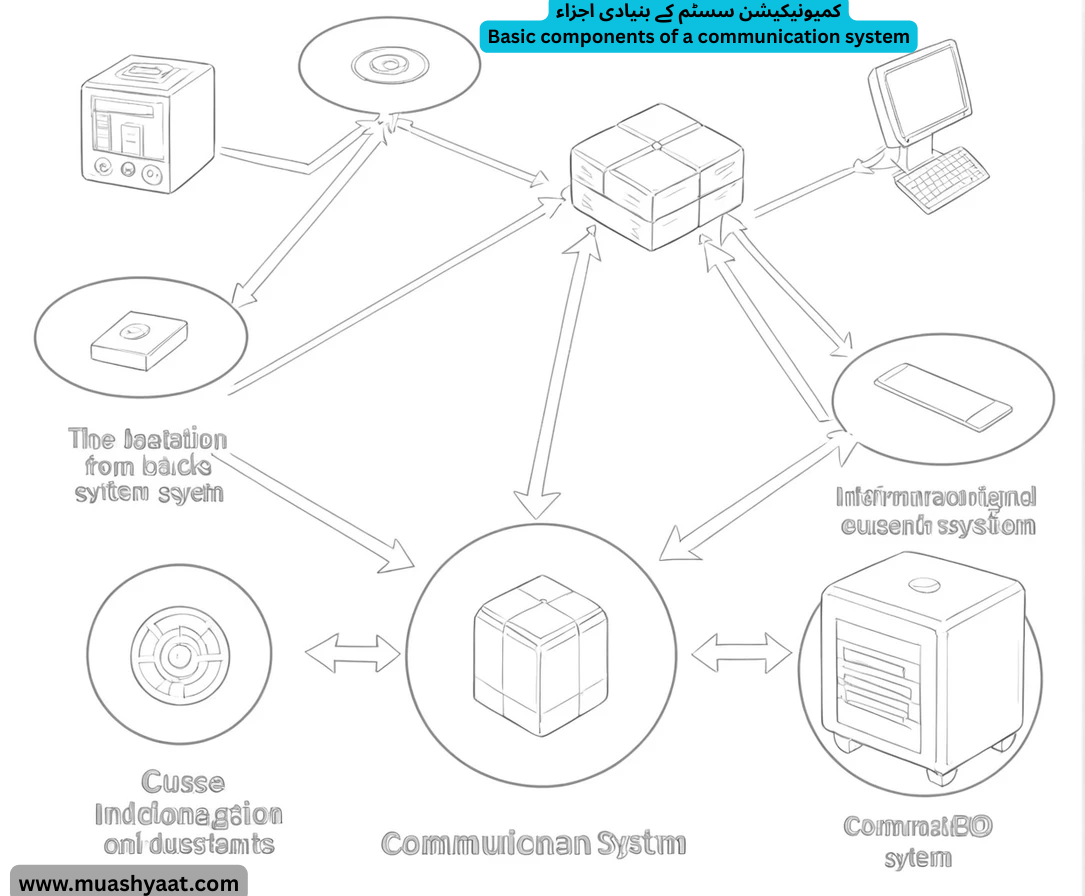
کمیونیکیشن سسٹم کے بنیادی اجزاء⇐ یقیناً۔ مواصلاتی نظام کے بنیادی اجزاء بنیادی تعمیراتی بلاکس ہیں جو معلومات کو ذریعہ سے منزل تک منتقل کرنے کے لیے درکار ہیں۔
یہ اجزاء ہر مواصلاتی نظام میں پایا جا سکتا ہے، ایک سادہ گفتگو سے لے کر ایک پیچیدہ عالمی سیٹلائٹ نیٹ ورک تک۔
پانچ ضروری اجزاء ہیں
معلومات کا ذریعہ
ٹرانسمیٹر
مواصلاتی چینل / میڈیم
وصول کنندہمنزل
ہر جزو کی تفصیلی بریک ڈاؤن
Basic components of a communication system Of course. The basic components of a communication system are the fundamental building blocks required to transmit information from a source to a destination.
- These components can be found in every communication system, from a simple conversation to a complex global satellite network.
The five essential components are:
- Information Source
- Transmitter
- Communication Channel / Medium
- Receiver
Destination
- Detailed Breakdown of Each Component
معلومات کا ذریعہ
یہ اس پیغام یا معلومات کی اصل ہے جس کو پہنچانے کی ضرورت ہے۔
فنکشن: خام ڈیٹا یا پیغام تیار کرتا ہے۔
مثالیں
ایک شخص بول رہا ہے (صوتی ڈیٹا)
ایک کمپیوٹر (ڈیجیٹل ڈیٹا جیسے ٹیکسٹ فائل یا ای میل)
ایک ویڈیو کیمرہ (ویڈیو اور آڈیو ڈیٹا)
ایک سینسر (درجہ حرارت، پریشر ریڈنگ)
Information Source
- This is the origin of the message or information that needs to be communicated.
- Function: Produces the raw data or message.
Examples:
- A person speaking (voice data)
- A computer (digital data like a text file or email)
- A video camera (video and audio data)
- A sensor (temperature, pressure readings)
ٹرانسمیٹر
ٹرانسمیٹر ذریعہ سے پیغام کو ایک ایسی شکل میں تبدیل کرتا ہے جو مخصوص چینل پر ترسیل کے لیے موزوں ہے۔ اس عمل میں اکثر انکوڈنگ اور ماڈیولیشن شامل ہوتی ہے۔
فنکشن: پیغام کو قابل منتقلی سگنل میں تبدیل کریں۔
کلیدی عمل
انکوڈنگ: معلومات کو ایک مخصوص شکل میں تبدیل کرنا (مثال کے طور پر، اینالاگ کو ڈیجیٹل میں، غلطی کی جانچ کرنے والے بٹس کو شامل کرنا)۔
ماڈیولیشن: معلوماتی سگنل کو کیریئر لہر پر متاثر کرنا (مثال کے طور پر، ریڈیو ٹرانسمیشن کے لیے، کیریئر لہر ایک اعلی تعدد برقی مقناطیسی لہر ہے)۔ یہ موثر تابکاری اور ملٹی پلیکسنگ کے لیے اہم ہے۔
Transmitter
- The transmitter transforms the message from the source into a form that is suitable for transmission over the specific channel. This process often involves encoding and modulation.
- Function: Convert the message into a transmittable signal.
Key Processes:
- Encoding: Converting the information into a specific format (e.g., analog to digital, adding error-checking bits).
- Modulation: Impressing the information signal onto a carrier wave (e.g., for radio transmission, the carrier wave is a high-frequency electromagnetic wave). This is crucial for efficient radiation and multiplexing.
مثالیں
ایک مائکروفون (صوتی لہروں کو برقی سگنل میں تبدیل کرتا ہے)
ایک موڈیم (ماڈیولیٹر-ڈیموڈولیٹر، کمپیوٹر سے ڈیجیٹل ڈیٹا کو ٹیلی فون لائن کے لیے ینالاگ سگنلز میں تبدیل کرتا ہے)
ایک ریڈیو ٹرانسمیٹر اینٹینا سسٹم
Examples:
- A microphone (converts sound waves into an electrical signal)
- A modem (Modulator-Demodulator, converts digital data from a computer into analog signals for a telephone line)
- A radio transmitter antenna system
مواصلاتی چینل میڈیم
یہ وہ جسمانی راستہ یا میڈیم ہے جس کے ذریعے منتقل شدہ سگنل ٹرانسمیٹر سے وصول کنندہ تک جاتا ہے۔
فنکشن: سگنل لے جانے کے لیے۔
اقسام
وائرڈ/گائیڈڈ: سگنل کی رہنمائی جسمانی راستے سے ہوتی ہے۔
مثالیں: بٹی ہوئی جوڑی کاپر کیبل (ایتھرنیٹ)، سماکشی کیبل (کیبل ٹی وی)، فائبر آپٹک کیبل (تیز رفتار انٹرنیٹ)۔
وائرلیس/غیر رہنمائی: سگنل کو بغیر کسی جسمانی موصل کے خلا میں پھیلایا جاتا ہے۔
مثالیں: ہوا (آواز، ریڈیو لہروں، مائیکرو ویوز کے لیے)، خلا کا خلا (سیٹیلائٹ سگنلز کے لیے)۔
Communication Channel / Medium
- This is the physical path or medium through which the transmitted signal travels from the transmitter to the receiver.
- Function: To carry the signal.
Types
- Wired/Guided: The signal is guided through a physical path.
- Examples: Twisted-pair copper cable (Ethernet), coaxial cable (cable TV), fiber optic cable (high-speed internet).
- Wireless/Unguided: The signal is propagated through space without a physical conductor.
- Examples: Air (for sound, radio waves, microwaves), vacuum of space (for satellite signals).
وصول کنندہ
یہ چینل سے سگنل کو قبول کرتا ہے، ڈی کوڈنگ اور ڈیموڈولیشن کے ذریعے اسے دوبارہ منزل کے لیے قابل استعمال شکل میں تبدیل کرتا ہے۔
فنکشن: موصول ہونے والے سگنل سے اصل پیغام کی تشکیل نو کریں۔
کلیدی عمل
ڈیموڈولیشن: ماڈیولڈ کیریئر ویو سے اصل معلوماتی سگنل نکالنا۔
ضابطہ کشائی: سگنل کو اس کے انکوڈ شدہ فارمیٹ سے اس کی اصل شکل میں تبدیل کرنا (مثال کے طور پر، ڈیجیٹل سے اینالاگ، غلطی کی اصلاح)۔
مثالیں
ایک اسپیکر (ایک برقی سگنل کو واپس آواز کی لہروں میں تبدیل کرتا ہے)
ایک ریڈیو ریسیور
وصول کرنے والا موڈیم
Receiver
- It accepts the signal from the channel, converts it back into a usable form for the destination through decoding and demodulation.
- Function: Reconstruct the original message from the received signal.
Key Processes:
- Demodulation: Extracting the original information signal from the modulated carrier wave.
- Decoding: Converting the signal from its encoded format back to its original form (e.g., digital to analog, error correction).
Examples:
- A speaker (converts an electrical signal back into sound waves)
- A radio receiver
- The receiving modem
منزل
یہ آخری نقطہ ہے جہاں موصولہ پیغام پیش کیا جاتا ہے یا استعمال کیا جاتا ہے۔ یہ معلومات کا مطلوبہ ہدف ہے۔
فنکشن: معلومات کا استعمال یا استعمال کریں۔
مثالیں
انسانی کان اور دماغ (ایک اسپیکر کو سننا)
کمپیوٹر مانیٹر (ایک موصول شدہ تصویر کی نمائش)
موصول ہونے والی فائل کو محفوظ کرنے والا کمپیوٹر
Destination
- This is the final point where the received message is presented or used. It is the intended target of the information.
- Function: Consume or utilize the information.
Examples:
- The human ear and brain (listening to a speaker)
- A computer monitor (displaying a received image)
- A computer saving a received file
شور کا تنقیدی کردار
شور ایک ناپسندیدہ رینڈم سگنل ہے جو چینل سے گزرتے ہوئے ٹرانسمٹڈ سگنل میں شامل ہو جاتا ہے۔ یہ کسی بھی مواصلاتی نظام کا ایک ناگزیر حصہ ہے اور اصل پیغام کو مسخ یا بگاڑ سکتا ہے۔
شور کے ذرائع: آسمانی بجلی، دیگر الیکٹرانک آلات سے مداخلت، اجزاء میں خامیاں، کائناتی ذرائع۔
سسٹم ڈیزائن کا ایک اہم مقصد سگنل ٹو نوائز ریشو (ایس این آر) کو زیادہ سے زیادہ کرنا ہے تاکہ یہ یقینی بنایا جا سکے کہ پیغام کو درست طریقے سے بازیافت کیا جا سکتا ہے۔
The Critical Role of Noise
- Noise is an unwanted random signal that gets added to the transmitted signal as it travels through the channel. It is an unavoidable part of any communication system and can distort or corrupt the original message.
- Sources of Noise: Lightning, interference from other electronic devices, flaws in the components, cosmic sources.
- A key goal of system design is to maximize the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) to ensure the message can be accurately recovered.
ہم أمید کرتے ہیں آپ کو “کمیونیکیشن سسٹم کے بنیادی اجزاء” کے بارے میں مکمل آگاہی مل گئی ہوگی۔۔۔
MUASHYAAAT.COM 👈🏻 مزید معلومات کیلئے ہمارے اس لنک پر کلک کریں
ہماری ویب سائٹ پر آنے کیلئےشکریہ